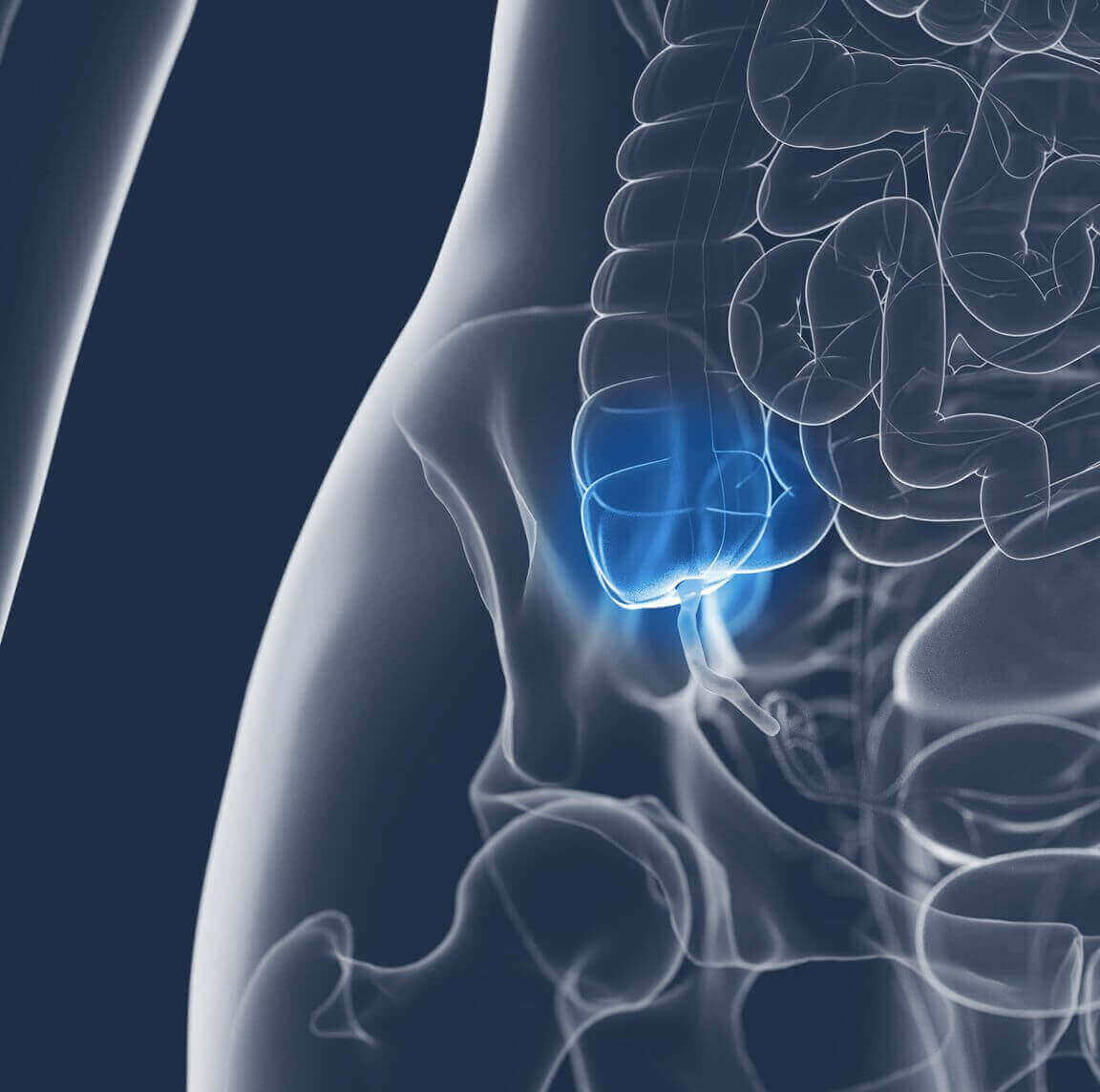
Appendix surgery, or appendicectomy, is carried out to treat appendicitis, a condition where the appendix becomes inflamed. The surgery can be performed as an open surgery or as laparoscopic surgery.
Appendicitis occurs when an obstruction in the appendix is present, resulting in bacteria multiplying within the appendix and causing it to be swollen, inflamed and filled with pus. It can happen at any age and is most common between the ages of 10 to 30. If left untreated, it may result in complications such as sepsis, peritonitis, gangrene or even death. Thankfully, appendix surgery can effectively aid in the treatment of appendicitis, and patients can live normally and resume their lives without their appendix.


What are the Symptoms of Appendicitis?
Abdominal pain is the hallmark symptom of appendicitis. The pain normally starts around the navel area and moves to the lower right area of the stomach. Over a few hours, the pain intensifies and becomes very severe.
Other symptoms include:
If you observe that you are experiencing the symptoms above, please visit an experienced surgeon for a detailed assessment.
How is Appendicitis Classified?














